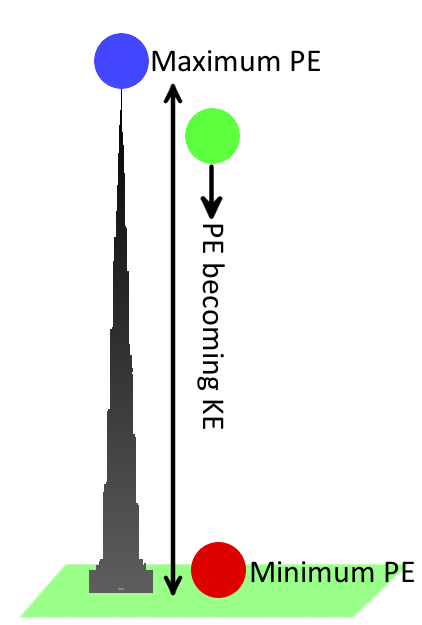
[新しいコレクション] right before the ball hits the ground all of the gravitational energy has become kinetic energy 123827
Projectile motion is the motion of an object thrown or projected into the air, subject to only the acceleration of gravity The object is called a projectile, and its path is called its trajectoryThe motion of falling objects, as covered in ProblemSolving Basics for OneDimensional Kinematics, is a simple onedimensional type of projectile motion in which there is no horizontal movementIf you look at this previous video where we plotted displacement versus time, you see after 2 seconds the ball went from being on the ground or I guess the thrower's hand all the way to its peak height And in the next 2 seconds, it took that same amount of time to go back down to the ground, which makes senseFor the coin, find (a) the maximum height reached, (b) its position and velocity 400 s after being released, and (c) the time before it hits the ground 18 A soft tennis ball is dropped onto a hard floor from a height of 150 m and rebounds to a height of 110 m
Kinetic And Potential Energy Energy Conversions
Right before the ball hits the ground all of the gravitational energy has become kinetic energy
Right before the ball hits the ground all of the gravitational energy has become kinetic energy-Chapter 4 Force and Motion Force may be defined as the cause of motion and deformationWhen a force is applied to an object, the object either moves or changes shape or bothIn most cases, it is not possible to detect the deformation by naked eyes at the molecular or atomic levelAlong the way the object being stretch or compress, kinetic energy is occurring After being compress or stretch, the object is release and again, kinetic energy is forming due to the restoring force If the surface is frictionless and there is no other resistance against the motion of the spring object, it would move back and forth forever



Energy Pie Charts Physics Blog
•Or • • when it hit the ground it would be moving at v = g •t =32 ft/s2 •95 sec = 305 ft/s or about 8 mph (watch out!) 2•distance time = g 2 2 1450 2900 906 95 32 / 32 ft time s ft s • ==== How high will it go?2 negative gradient or line slopes downwards (left to right) B1 8(b)(ii) 1 0 s ⩽ time ⩽ 090 s B1 2 area or counting squares or ½bh in some form C1 37 s ⩽ distance ⩽ 41 m A1 8(b)(iii) ball hits ground or short time for deceleration or large force or ground is hard B1Doublejumping right before hitting the ground, grabbing a rope, falling in cobwebs or liquids, opening an umbrella midfall, using a device to teleport back home while falling, and even using a grappling hook down and shooting one's self down faster are all valid ways to avoid taking a hit from landing After entering Hardmode, equipping wings
The bowling ball has a greater mass, so there's more stuff for gravity to act on In that sense, gravity is pulling on it more In that sense, gravity is pulling on it more But it still doesn'tRotational kinetic energy and gravitational kinetic energy at the height HA Ball B, however, has friction on the ramp to slow the rotation so that at height HB, Ball B has only gravitational potential energy;A 10 kg bowling ball at a height of 100 m has potential energy due to gravity Potential energy = mgh = 10 kg x 98 m/s2 x10 m = 9800 J As it falls it speeds up converting potential energy into kinetic energy Right before it hits ground all the potential energy has become kinetic energy = 9800 J
All of the original kinetic energy, both rotational and translational, is now gravitational potential energy Ball B, therefore, has• linear kinetic energy • rotational kinetic energy • sound energy • thermal energy bouncy ball compressed when it hits ground A spring loaded toy is pressed down on top of a desk Mechanical Energy is the _____ of rotational and linear kinetic, and _____ and gravitational potential energy sum, elastic(Answer Prior to the drop, an elevated egg has a large amount of gravitational potential energy due to its height above the ground When it is dropped, that the energy is transferred from potential to kinetic Right before the egg hits the egg catcher, (nearly) all the potential energy has been converted to kinetic energy)


Http Www West Windsor Plainsboro K12 Nj Us Common Pages Displayfile Aspx Itemid



Energy Wikipedia
A perfectly inelastic collision is one in which two objects colliding stick together, becoming a single object For instance, two balls of sticky putty thrown at each other would likely result in perfectly inelastic collision the two balls stick together and become a single object after the collision Unlike elastic collisions, perfectly inelastic collisions don't conserve energy, butBut remember the kinematic equations only apply over periods of constant acceleration As soon as the ball touches the ground, the ground causes it to slow down very quickly—it no longer has a downward acceleration of g So Point 3 is the point just before the ball touches the groundEarth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor lifeAbout 29% of Earth's surface is land consisting of continents and islandsThe remaining 71% is covered with water, mostly by oceans but also by lakes, rivers, and other fresh water, which together constitute the hydrosphereMuch of Earth's polar regions are covered in ice



Potential Energy And Conservation Of Energy Boundless Physics



Conservation Of Energy In Projectile Motion Examples Analysis Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Pikmin 2 WalkthroughJust before he hits ground, he has large KE (large speed) This gets transformed into heat the other half of the PE has become KE And another example sun and then to earthAssuming a system consisting of just the ground (gravitational force) and the ball, we can apply the Law of Conservation of Energy, which states that, in any closed system, the net energy (kinetic potential) is constant Here, we need only to find the energy at the two endpoints of motion and equate the two Energy at Peak of Motion


Q Tbn And9gct Gdtgx3beohozxgncscpqzs8uythlltvfdocr7cek9fwxw0r9 Usqp Cau



Conservation Of Energy The Cosmic Universe Openstax Cnx
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy it possesses due to its motion The kinetic energy of the ball will continue increasing as the ball gains momentum, until it finally collides with a surface When the ball collides, the kinetic energy is transformed into other forms of energy When a ball hits a surface, some energy is transA set of equations describe the resultant trajectories when objects move owing to a constant gravitational force under normal Earthbound conditionsFor example, Newton's law of universal gravitation simplifies to F = mg, where m is the mass of the body This assumption is reasonable for objects falling to earth over the relatively short vertical distances of our everyday experience, but isEarth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor lifeAbout 29% of Earth's surface is land consisting of continents and islandsThe remaining 71% is covered with water, mostly by oceans but also by lakes, rivers, and other fresh water, which together constitute the hydrosphereMuch of Earth's polar regions are covered in ice



Potential Energy Potential And Kinetic Energy Siyavula
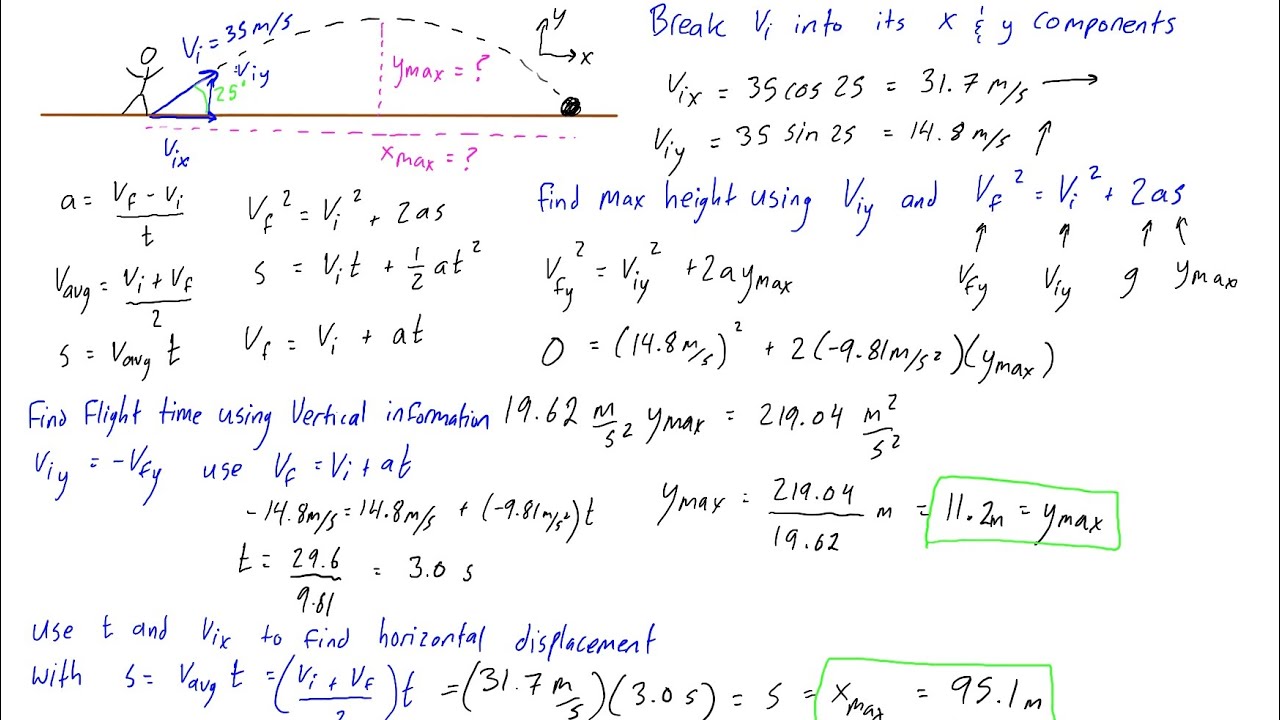


Projectile Motion Example Problem 3 Kicking A Soccer Ball Youtube
Notice that the total energy is the same in both cases, but just after the ball is thrown, all its energy is kinetic When it reaches the maximum height, all the energy has now been converted intoA student releases a ball from a height of 15 m above the floor Which of the following statements best describes the energy of the ball as it falls?And we want the negative square root of that in that situation, when the height is 5 meters So if you jump off of a onestory commercial building, right at the bottom, or if you throw a rock off that, right at the bottom, right before it hits the ground, it will have a velocity of negative 99 meters per second



Conservation Of Energy In Projectile Motion Examples Analysis Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


Practical Report Bounce Efficiency
Less than 7 J you are holding a 1 kg rock and standing at the top of a cliff you drop the rock off the cliff and it falls a distance 10 m ignore air resistance what is the change in kineticWe see that it has a potential energy of 100 joules All of this potential energy gets converted to kinetic energy as the ball falls down the ramp Knowing this, we can determine the velocity the ball has at the bottom of the ramp by setting the potential energy equal to the kinetic energy We substitute the known mass and solve forA ball is dropped from rest and falls to the floor The initial gravitational potential energy of the ballEarthfloor system is 10 J The ball then bounces back up to a height where the gravitational potential energy is 7 J What was the mechanical energy of the ballEarthfloor system the instant the ball left the floor 0 J;



Modelling Instruction For University Physics Examining The Theory In Practice Iopscience
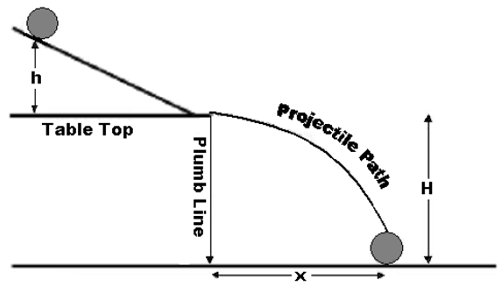


Energy Of A Rolling Object
The ball below has potential energy because of the Earth's gravitational pull on it and its position above the ground This is called gravitational potential energy (PE) If the ball falls, it gains kinetic energy (KE) Both PE and KE can be calculated Calculating PE The gravitational potential energy of the ball on the left is equal to the workEnergy as a tool for mechanics problem solving The application of the conservation of energy principle provides a powerful tool for problem solving Newton's laws are used for the solution of many standard problems, but often there are methods using energy which are more straightforward For example, the solution for the impact velocity of a falling object is much easier by energy methodsOnce the appropriate equation has been selected, the physics problem becomes transformed into an algebra problem By substitution of known values, the equation takes the form of060 m = (0 m/s)•t 05•(98 m/s/s)•t 2 Since the first term on the right side of the equation reduces to 0, the equation can be simplified to


Aswarphysics Weebly Com Uploads 4 6 2 1 University Physics With Modern Physics 13th Sears Zemansky Part2 Pdf



What Is Gravitational Potential Energy Article Khan Academy
When two balls of different masses are dropped from equal height, they reach the ground at the same time Can anyone explain this in terms of physics?How fast was the piano right before it hit the roof?Which has greater kinetic energy, an adult running at 3 mi/hr or a •What happens to the energy when he hits the ground?


Web Mit Edu Yczeng Public Workbook 1 full Pdf


Stacked Ball Drop Lessons In Conservation Of Energy And Momentum Sciphile Org
Here we look at Potential Energy (PE) and Kinetic Energy (KE)At impact, the cue ball stops, but transfers all of its momentum and kinetic energy to the other ball, resulting in the hit ball rolling with the initial speed of the cue ball In an inelastic collision, momentum is conserved, but the total kinetic energy of the system is not conserved When the collision occurs, some kinetic energy isThe bowling ball has a greater mass so it also has a greater gravitational force You can calculate this gravitational force as the product of the mass (m) and the gravitational field (g)



Gravitational Potential Of The Body Of Mass M At A Height H From Surface Of Earth Of Radius R Is Take G Acceleration Due To Gravity At Earth S Surface



Mastering Physics Solutions Chapter 8 Potential Energy And Conservation Of Energy A Plus Topper
Potential and Kinetic Energy Energy Energy is the capacity to do work The unit of energy is J (Joule) which is also kg m 2 /s 2 (kilogram meter squared per second squared) Energy can be in many forms!Newton's cradle with two balls of equal weight and perfectly efficient elasticity The left ball is pulled away and let go Neglecting the energy losses, the left ball strikes the right ball, transferring all the velocity to the right ball Because they are the same weight, the same velocity indicates all the momentum and energy are alsoAssuming a system consisting of just the ground (gravitational force) and the ball, we can apply the Law of Conservation of Energy, which states that, in any closed system, the net energy (kinetic potential) is constant Here, we need only to find the energy at the two endpoints of motion and equate the two Energy at Peak of Motion



Conservation Of Energy The Cosmic Universe Openstax Cnx



Energy Cat Vs The Rubber Ball
A 10 kg bowling ball at a height of 100 m has potential energy due to gravity Potential energy = mgh = 10 kg x 98 m/s2 x10 m = 9800 J As it falls it speeds up converting potential energy into kinetic energy Right before it hits ground all the potential energy has become kinetic energy = 9800 JBecause gravity has the most time to do its job when the balls are dropped from 75 centimeters, these balls have the most kinetic energy by the time they hit the ground When the ball hits the ground, all that kinetic energy has to go somewhere A lot of it goes back into the ball, giving it more force to pop back up into the air—so the higher the potential energy, the higher the kinetic energy, and the higher the kinetic energy, the higher the bounce!When you throw or drop a tennis ball to the ground, it has a certain amount of kinetic energy when it hits the ground (this is energy of moving objects) When it hits the ground, some energy is transferred into the ground or the air as heat or sound The larger the energy left in the ball, the higher it will bounce on the way back up



Conservation Of Mechanical Energy Mechanical Energy Siyavula



A Ball Of Mass 8 Kg Is Dropped From A Height Of 10 M What Is The Velocity With Which It Strikes The Ground Quora
Energy skate park simulation (Conservation of Energy) If the skater is placed at the five meter mark on the ramp, he will travel only five meters high on the other side of the track The skater's kinetic energy increases as he moves down the ramp The skater's kinetic energyInstead it falls at a constant speed, called the terminal velocity, all the way to the ground Pennies are flat, so they experience a lot of air resistance, and they are light, so it doesn't takeKinetic energy, gravitational potential energy and conservation of energy If an object, such as a ball is lifted above the ground it has gravitational potential energy If the ball is then dropped



Energy Pie Charts Physics Blog



Collins Cambridge International As A Level Physics By Collins Issuu
The ball below has potential energy because of the Earth's gravitational pull on it and its position above the ground This is called gravitational potential energy (PE) If the ball falls, it gains kinetic energy (KE) Both PE and KE can be calculated Calculating PE The gravitational potential energy of the ball on the left is equal to the workA ball is dropped in the atmosphere where air resistance is present as it falls it loses 7 J of potential energy how much kinetic energy did it gain?Out how long it would take the ball to fall all the way to the ground (1450 ft) Ætime = square root of (2 x distance/g) Look at below!



7 3 Work Energy Theorem University Physics Volume 1



2 7 Falling Objects College Physics Openstax
A soccer ball is kicked off the ground with a velocity of 18 m/s at an upward angle of 35 degrees Using a gravitational constant g = 98 m/s{eq}^2 {/eq}, calculate the followingLightning forks and rejoins itself over Table Mountain and Lion's Head in Cape Town, South Africa Central Africa is the area of the world where lightning strikes most frequentlySection 8–2 Topic Kinetic Energy of a System Type Conceptual 12 A golf ball and a PingPong ball are dropped in a vacuum chamber When they have fallen halfway to the floor, they have the same A) speed B) potential energy C) kinetic energy D) momentum E) speed, potential energy, kinetic energy, and momentum Ans A


Application And Practice Questions


Potential And Kinetic Energy
In a cricket match, a 2metertall pace bowler throws a yorker ball with a horizontal velocity of m/s \text{ m/s} 2 0 m/sThe batsman hits the ball with twice the horizontal velocity of the ball at an angle of 45 ∘ {45}^\circ 4 5 ∘ with the horizontal The ball lands just in front of a fielder, who kicks the ball with his foot at an angle of 30 ∘ {30}^\circ 3 0 ∘ with the(A) Its potential energy is changed to kinetic energy (B) The total amount of its mechanical energy increases (C) Its kinetic energy is changed to potential energySystem then the only kind of energy it could have would be kinetic energy I can write this as be a gravitational potential energy but


A Ball Of Mass 8 Kg Is Dropped From A Height Of 10 M What Is The Velocity With Which It Strikes The Ground Quora



What Is Kinetic Energy Live Science
Physics College Physics An object is dropped from a height of 750 m above ground level (a) Determine the distance traveled during the first second (b) Determine the final velocity at which the object hits the ground (c) Determine the distance traveled during the last second of motion before hitting the groundEarth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor lifeAbout 29% of Earth's surface is land consisting of continents and islandsThe remaining 71% is covered with water, mostly by oceans but also by lakes, rivers, and other fresh water, which together constitute the hydrosphereMuch of Earth's polar regions are covered in ice



Gravity And Mechanical Energy Physics Grade 10 Caps 11 Openstax Cnx


The Pitcher The Physics Of Baseball



3 5 Free Fall University Physics Volume 1



What Are The Physics Behind Bouncing Balls



Science 10 Physics Flashcards Quizlet


Http Www West Windsor Plainsboro K12 Nj Us Common Pages Displayfile Aspx Itemid



At Which Point Will The Potential And Kinetic Energy Be The Same In A Free Falling Body Quora


Http Wwphs Sharpschool Com Common Pages Displayfile Aspx Itemid



Conservation Of Energy In Projectile Motion Examples Analysis Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



A Ball Of Mass 0 2 Kg Is Dropped From A Height Of 10 M How Much Mechanical Energy Does It Have Right Brainly Com


Http Www West Windsor Plainsboro K12 Nj Us Common Pages Displayfile Aspx Itemid



Potential Energy Potential And Kinetic Energy Siyavula



Aqa Gcse 9 1 Physics Student Book By Collins Issuu



Physical Science Review 1 One Of The Most Effective Agents Of


If The Energy Of A Ball Falling From A Height Of 10 Meters Is Reduced By 40 How High Would It Rebound Quora
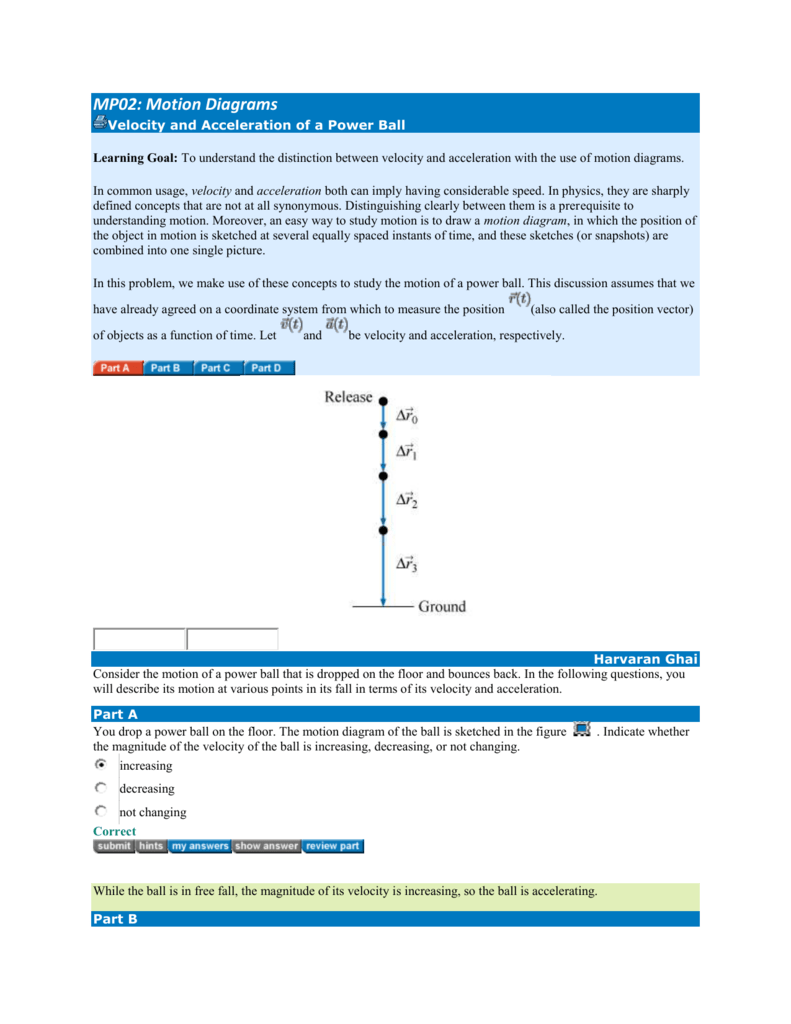


Mastering Physics Answers


Kinetic And Potential Energy Energy Conversions



Gravity And Mechanical Energy Physics Grade 10 Caps 11 Openstax Cnx
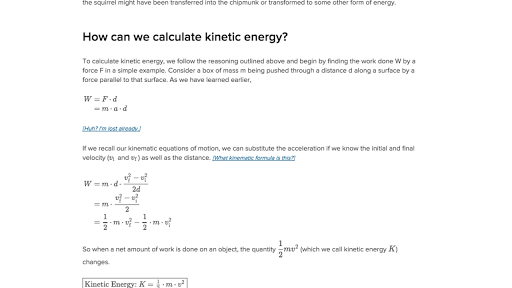


What Is Kinetic Energy Article Khan Academy


Sph4c



Physics Puzzles With Answers



Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions For Chapter 4 Work And Energy Free Pdf


Http Sjutsscience Weebly Com Uploads 3 7 4 5 Kinetic And Potential E Skills Key Pdf
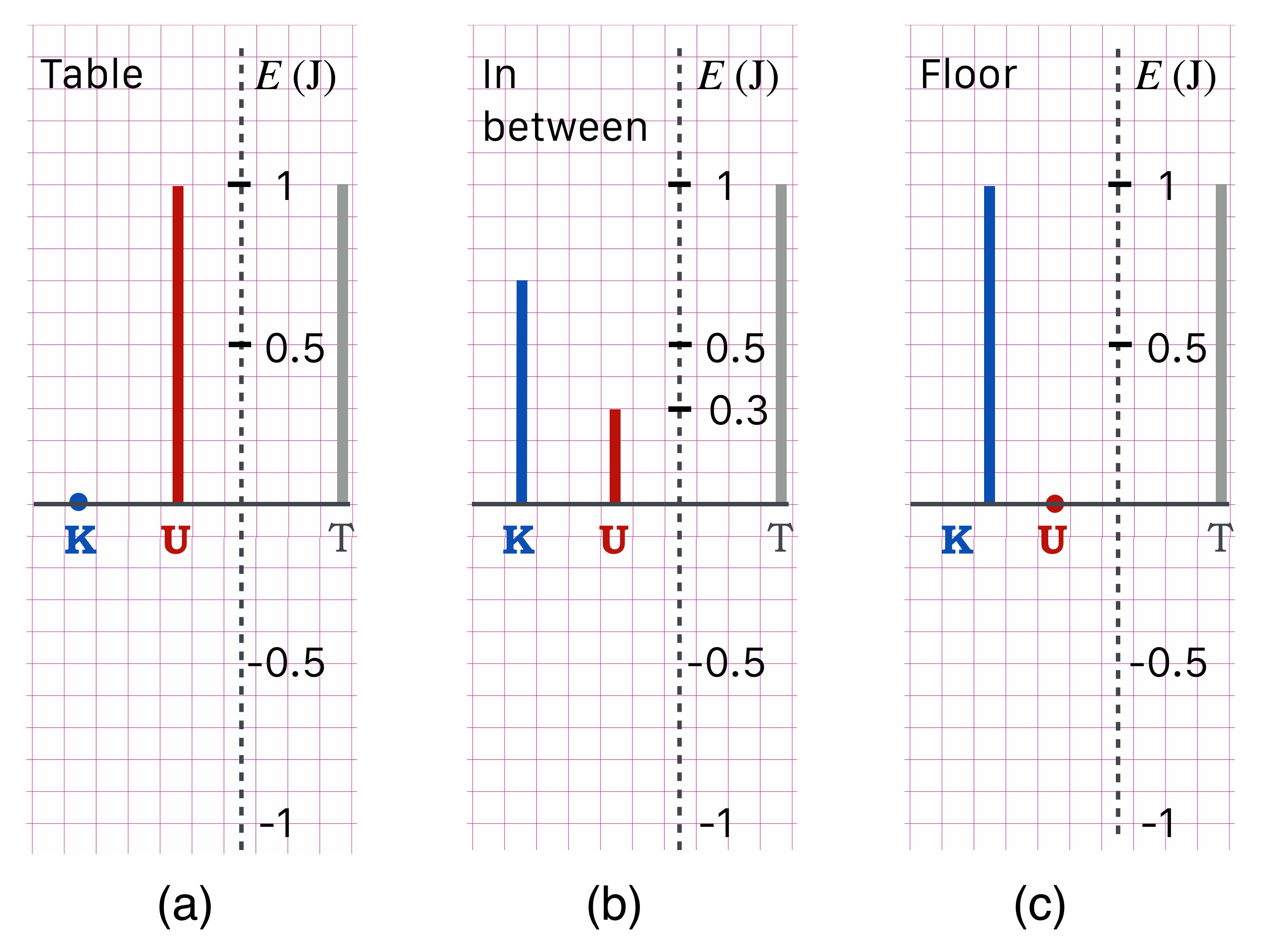


Lesson 7 Energy It Just Keeps Going And Going


Bar Chart Illustrations
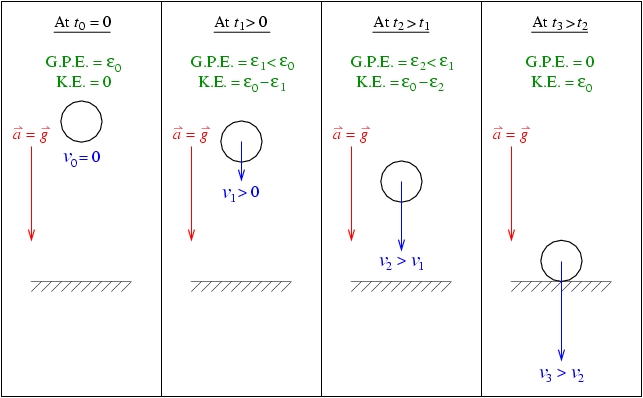


How Things Work Phys1055 Revealing The Magic In Everyday Life Phys0612
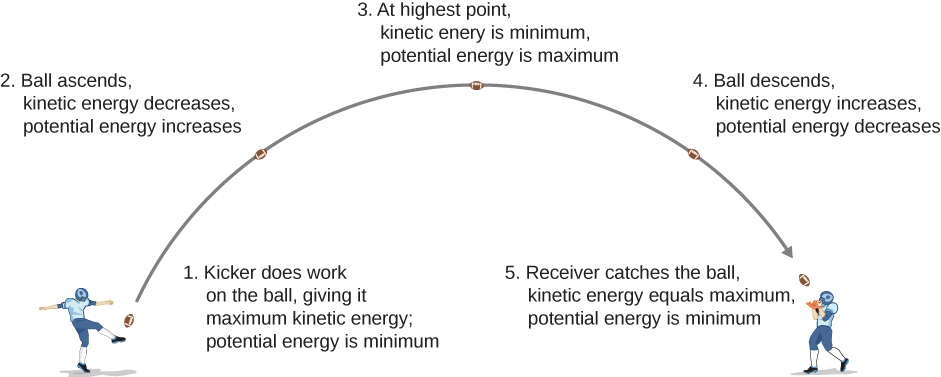


8 1 Potential Energy Of A System University Physics Volume 1



Conservation Of Energy In Projectile Motion Examples Analysis Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Potential Energy Ck 12 Foundation
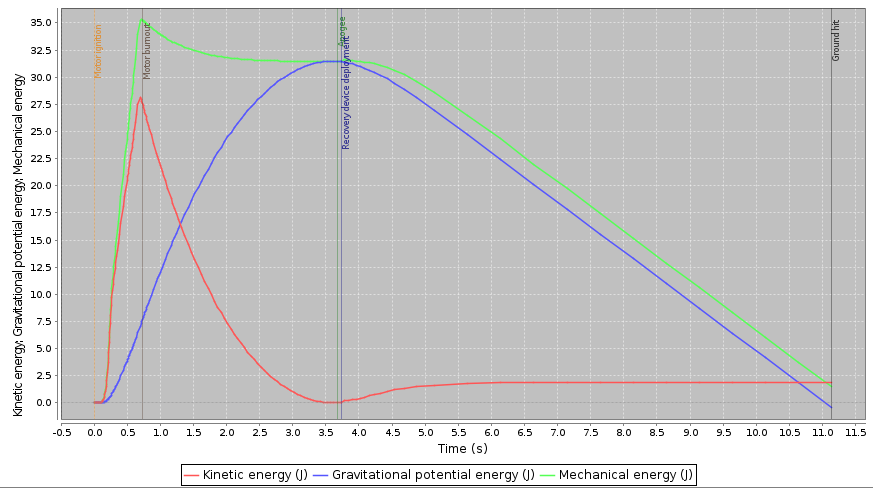


What Is Conservation Of Energy Article Khan Academy


Ask The Physicist


If We Drop Different Weights From Same Height Which Will Fall First To Ground Quora


What Is Electricity Learn Sparkfun Com


Bar Chart Illustrations


1


Www Pearsonhighered Com Assets Samplechapter 0 1 3 4 Pdf


Kinetic And Potential Energy Energy Conversions



Energy Pie Charts Physics Blog


Stacked Ball Drop Lessons In Conservation Of Energy And Momentum Sciphile Org
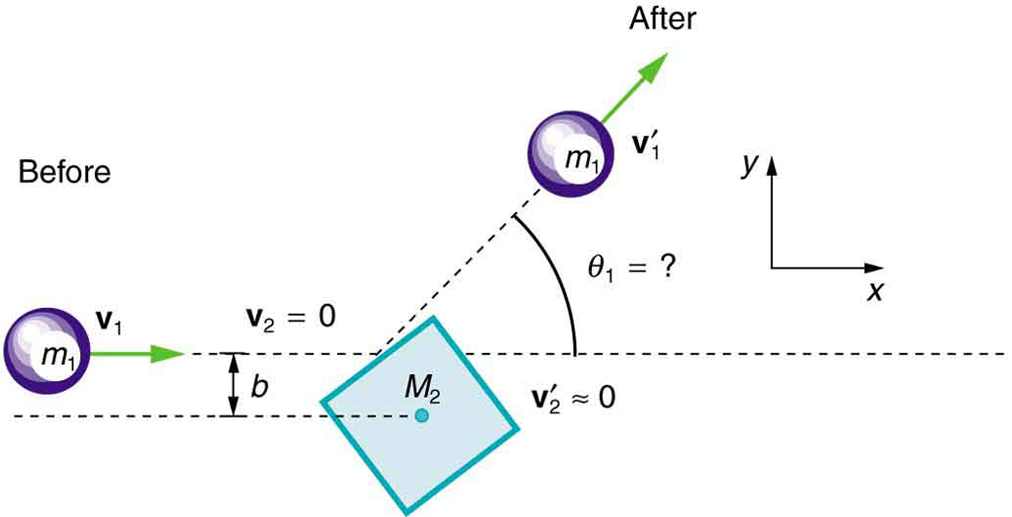


8 Linear Momentum And Collisions Exercises Physics Libretexts



Conservation Of Energy The Cosmic Universe Openstax Cnx


Web Mit Edu Yczeng Public Workbook 1 full Pdf


A 2kg Stone Is Dropped From The Top Of A m Building If G 10m S Of What Height Does The Potential Energy Becomes Equal To Kinetic Energy What Is The Potential Energy Of



Sph4c


8 1 Potential Energy Of A System University Physics Volume 1



Gravitational Potential Energy Definition Formula Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


Ask The Physicist
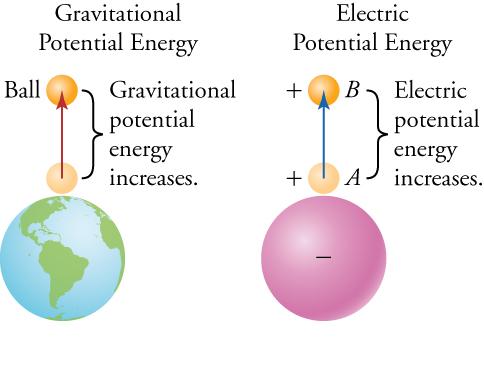


18 4 Electric Potential Texas Gateway
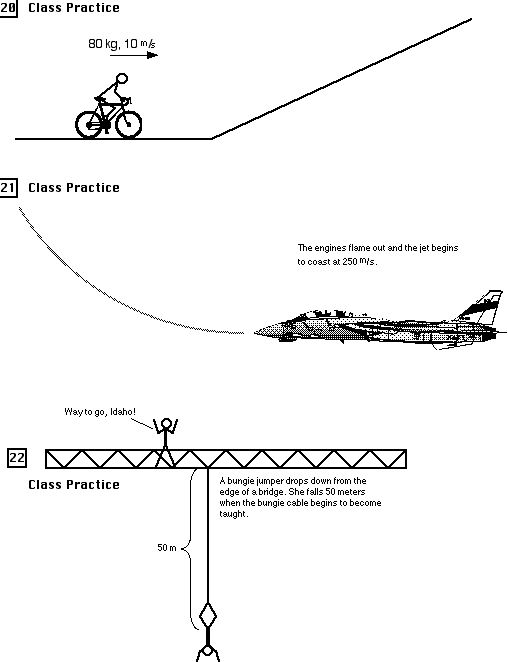


Ahs Mechanical Energy Worksheet



Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions For Chapter 4 Work And Energy Free Pdf



Falling Objects Physics



Mastering Physics Solutions Chapter 8 Potential Energy And Conservation Of Energy A Plus Topper


Q Tbn And9gctsw9deqlqwnplo59akvylm 41obadsn5ztneoy2ecgvq Pr8vg Usqp Cau



Energetic 2 Ball Bounces Scientific American


Energy Course Hero



Potential Energy Potential And Kinetic Energy Siyavula


Http Iopscience Iop Org Article 10 10 1361 6404 c236 Pdf


If The Energy Of A Ball Falling From A Height Of 10 Meters Is Reduced By 40 How High Would It Rebound Quora



What Is Gravitational Potential Energy Article Khan Academy



Unit 2 Energy And Momentum Classconnect



Does A Thrown Ball Have Kinetic Energy At The Top Of The Curve Physics Stack Exchange


Sph4c



Practice Problem Kinetic And Potential Energy Of A Ball On A Ramp Youtube


Q Tbn And9gcstaasuj3lqdptiptwtrjislccl85impcbqyrb08bbm6vzecod7 Usqp Cau


Web Phys Ksu Edu Fascination Chapter9 Pdf
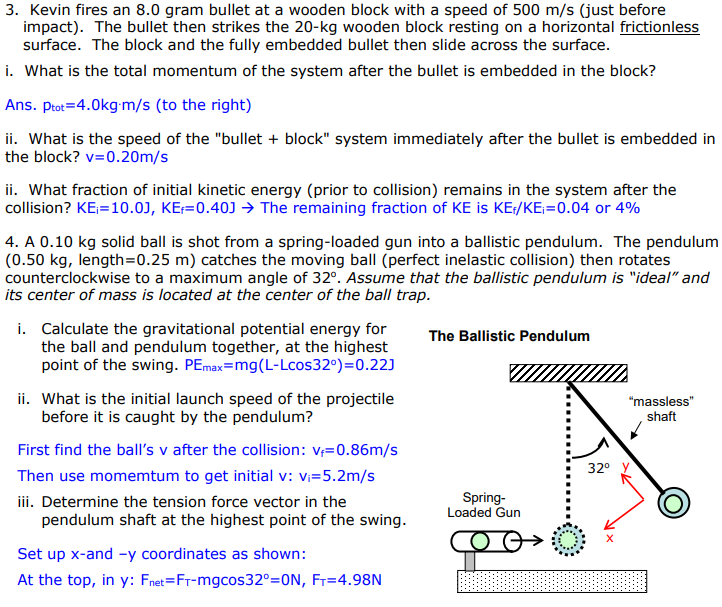


Solved Im Not Really Sure How To Find Question 3 Part Iii Chegg Com



Law Of Conservation Of Energy Video Khan Academy



Gravitational Potential Energy S Cool The Revision Website



Sph4c



13 3 Gravitational Potential Energy And Total Energy University Physics Volume 1


What Is Conservation Of Energy Article Khan Academy


The Bounce Factory Hacker Noon


Kinetic And Potential Energy Energy Conversions



Physics Chapter 8 Answers Potential Energy Kinetic Energy


コメント
コメントを投稿